The realm of vehicular technology has seen a paradigm shift with the advent of GPS vehicle tracking, a tool that has transformed the way we interact with and manage our vehicles.
From personal cars to expansive fleets, the inclusion of GPS (Global Positioning System) has heralded a new era of efficiency, safety, and convenience. This article offers a deep dive into the world of GPS for cars, exploring its functionality, benefits, and the diverse applications that it supports.
The Mechanics of GPS Vehicle Tracking
Understanding the mechanics of GPS vehicle tracking is essential for appreciating how this technology has revolutionized the management and safety of vehicles. The system hinges on the Global Positioning System (GPS), a network of satellites that provide geolocation and time information to a GPS receiver anywhere on or near the Earth. Here’s a closer look at how this intricate system functions.
1. Satellite Network:
GPS relies on a constellation of about 30 satellites orbiting the Earth. These satellites, operated by the U.S. Department of Defense, are positioned in such a way that at any given time, a Vehicle GPS tracking on Earth can receive signals from at least four of them. These satellites are constantly transmitting signals back to Earth.
2. GPS Receivers in Vehicles:
Each vehicle equipped with tracking has a receiver. This receiver’s job is to continuously scan for signals from the satellites overhead. When the receiver picks up signals from at least four satellites, it can accurately determine the vehicle’s location.
3. Triangulation for Location Determination:
The process of determining the vehicle’s location is known as triangulation. Each satellite signal includes information about the satellite’s location and the exact time the signal was transmitted.
The receiver uses the time difference between the signal’s transmission and reception to calculate how far the signal has traveled. By knowing the distance from several satellites, the receiver can pinpoint the vehicle’s precise location through a process of triangulation.
4. Data Transmission to User Interface:
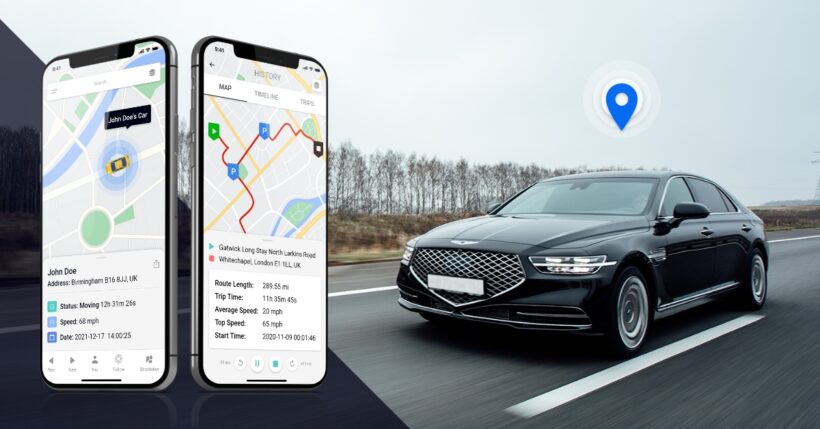
Once the vehicle’s position is determined, this information is usually transmitted via cellular or satellite networks to a central server. From there, the data can be accessed by users through specialized software applications, which can be web-based or mobile apps. This allows vehicle owners or fleet managers to view the vehicle’s location in real-time.
5. Additional Information Gathering:
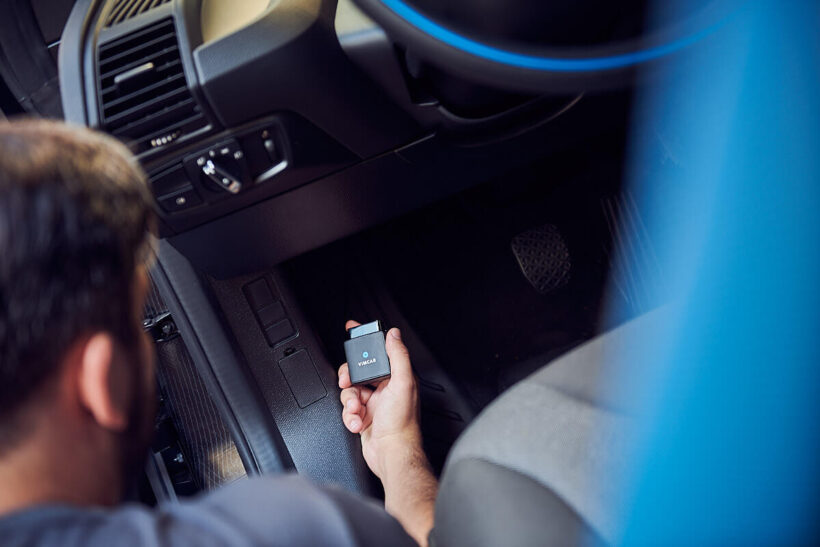
Modern GPS systems can gather more than just location data. They can also collect information on the vehicle’s speed, direction, idle time, and sometimes even mechanical health indicators. Some systems integrate with the vehicle’s onboard diagnostics (OBD) port to provide real-time alerts on vehicle health, fuel consumption, and other critical data.
6. Advanced Features:
Advanced GPS solutions offer additional features like geofencing, where the vehicle owner can set up virtual boundaries and receive alerts when the vehicle enters or exits these areas. Route history, driver behavior analysis, and customizable reports are other sophisticated functionalities that can be leveraged through GPS systems.
7. Privacy and Security Considerations:

While vehicle tracking offers numerous benefits, it also raises privacy concerns. It’s crucial for users to understand who has access to their tracking data and how it’s being used. Secure encryption of data transmission and strict privacy policies are essential to protect user data.
Key Features of GPS Car Tracking
- Real-Time Monitoring: The cornerstone of tracking is its ability to provide real-time updates on a vehicle’s location, offering peace of mind to vehicle owners and fleet managers.
- Route Optimization: For businesses, tracking aids in plotting the most efficient routes, leading to reduced fuel costs and time savings.
- Enhanced Security: tracking is a formidable tool against vehicle theft, allowing for prompt location and recovery. Geofencing features further enhance this by alerting owners when vehicles enter or leave predefined areas.
- Maintenance Management: Some tracking solutions offer diagnostics on vehicle health, prompting maintenance checks when needed, thus extending the lifespan of the vehicle.
- Insurance Advantages: Many insurers offer lower premiums for vehicles equipped with tracking systems due to their enhanced security and recovery capabilities.
Applications Across Various Domains

- Individual Use: For personal vehicle owners, tracking provides a sense of security and is particularly useful for monitoring new or young drivers.
- Fleet Management: Commercial fleets use tracking to oversee operations, ensure compliance with driving regulations, and enhance customer service through precise delivery tracking.
- Rental Services: Car rental companies implement tracking to monitor their fleets, prevent unauthorized usage, and maintain the safety of their vehicles.
- Emergency Response: GPS is critical for emergency vehicles like ambulances, enabling them to reach their destinations quickly and efficiently.
Selecting an Appropriate GPS Tracking System
When choosing a GPS solution, consider the following:
- Type of Tracking: Decide between real-time and passive tracking systems, based on your specific needs.
- Software Quality: Opt for a system with reliable and detailed mapping capabilities.
- User Interface: The system should be intuitive and easy to navigate for efficient usage.
- Integration Features: Assess if the tracking system can seamlessly integrate with other operational tools you use.
- Cost Effectiveness: Weigh the features against the cost to ensure a beneficial investment.
The Road Ahead for GPS Vehicle Tracking

The trajectory of GPS is set towards greater integration with emerging technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI). Future developments may include predictive analytics for vehicle maintenance, enhanced traffic management through real-time data, and deeper integration with smart city infrastructures, further revolutionizing vehicle tracking.
Conclusion
The implementation of GPS in vehicles is a significant leap forward in automotive technology. It offers not just a means to track location but a comprehensive solution that enhances security, improves operational efficiency, and provides valuable insights into vehicle usage.
As the technology evolves, vehicle tracking is poised to become an indispensable tool in the automotive industry, reshaping how we interact with and manage our vehicles. For anyone looking to optimize their vehicle’s potential, GPS stands as a testament to the power of technology in driving forward modern transportation solutions.
