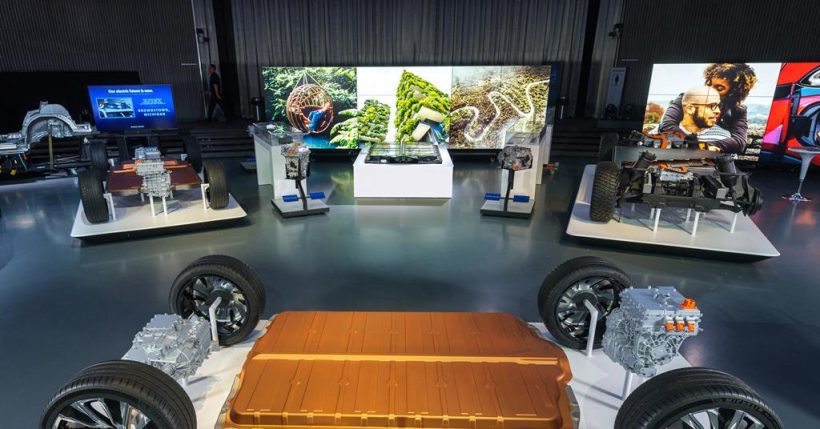
Batteries are the key component of Electric Vehicles, and the research and development for new batteries for EVs is underway. The batteries used for electric vehicles are the most important components of an electric vehicle. The exploration and improvement of new battery types are constantly ongoing because it offers the greatest potential for increasing range and reducing costs in Electric Vehicles.
Essentially, electric Vehicles are powered by batteries, which provide the energy needed to propel the car. There are three important factors in evaluating the performance of an EV battery. These factors include capacity, power, and cost. For more info check https://simonlucas.co.nz/phev-cars.
What’re the Features of an EV Battery?
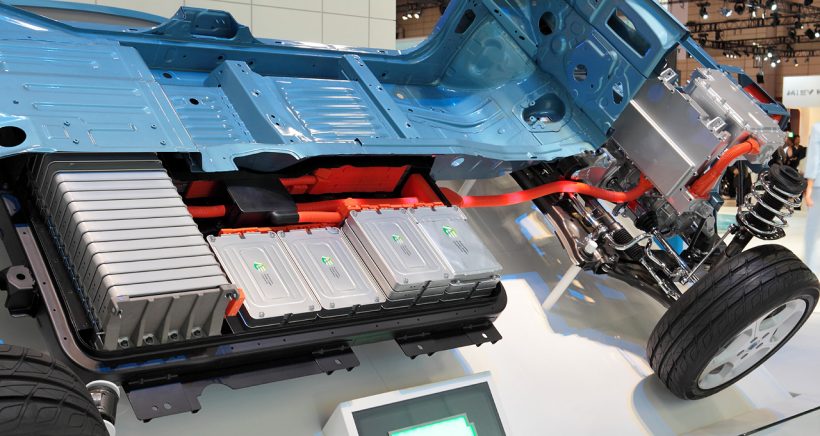

Energy density-The higher the density, the more miles you can drive on a single charge. The best EVs have a range between 100-300 mi. Most hybrids, around 50 mi, and gas cars get only 15-20 mi.
Longest lasting batteries are nickel-metal hydride and lithium-ion. Lead-acid batteries have poor energy density but can last for thousands of cycles.
What Batteries are Common in Electric Vehicles?
Presently, the batteries used in most electric vehicles are lithium-ion cells which use a liquid electrolyte to move charges between the electrodes. Although there are different combinations depending on the battery type, these liquid cells generally use a graphite anode and nickel-cobalt-aluminium (NCA) cathode.
This provides a good basic understanding of what batteries do, but battery technology is still developing rapidly as different chemistries are being researched. Auto manufacturers have claimed that their existing lithium-ion batteries will last ten years or 150,000 miles in EVs before needing replacement. However, they also state that they expect improvements to be made during this period. Therefore, some models may not need replacement at all.
The type of battery that is used in PHEV cars must power a vehicle for 30-40 miles, provide regenerative braking and recharge using a standard 120 V outlet
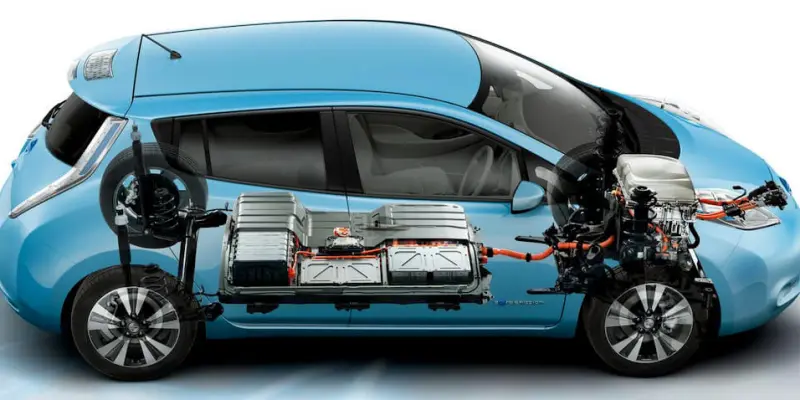

These requirements are what currently defines PHEVs and make them so popular. There are three main types of batteries capable of meeting the needs of PHEV cars. These include nickel-metal hydride, lithium polymer, and lithium-ion. Nickel-metal hydride batteries have been around longer than either type of lithium battery.
However, they struggle to meet the demand that comes with powering an electric car designed for long-distance travel. Lithium polymer batteries are another option. But they also struggle to provide enough energy while recharging quickly enough through regenerative braking or by plugging into a home electrical outlet.
Lithium-ion, also known as Li-ion batteries, on the other hand, can meet all these demands quite well and last for about 300 charge cycles before needing replacement. These types of batteries offer the best balance between weight, portability, and cost-effectiveness in relation to the amount of power they can store under pressure.
Lithium-ion technology was developed in the 1970s and has been increasingly used by the military and space program
The battery cells comprise lithium, aluminium, copper, carbon, and cobalt. The lithium-ion battery chemistry was first developed in the 1970s. At that time, Sony was working on developing a rechargeable lithium battery for use in video cameras.
After that, it took another 20 years before lithium-ion batteries were available commercially at an affordable price. They were first used in laptops and cell phones.
The popularity of these batteries grew as they became smaller and more powerful over time, resulting from continued research. Today they are used in electric vehicles because they can deliver higher energy densities than other types of rechargeable batteries like lead-acid or nickel-metal hydride (NiMH). When it comes to high power density applications like satellites and spacecraft, lithium-ion batteries are the preferred choice for powering them due to their lightweight.
All new electric vehicles are designed with lithium-ion batteries
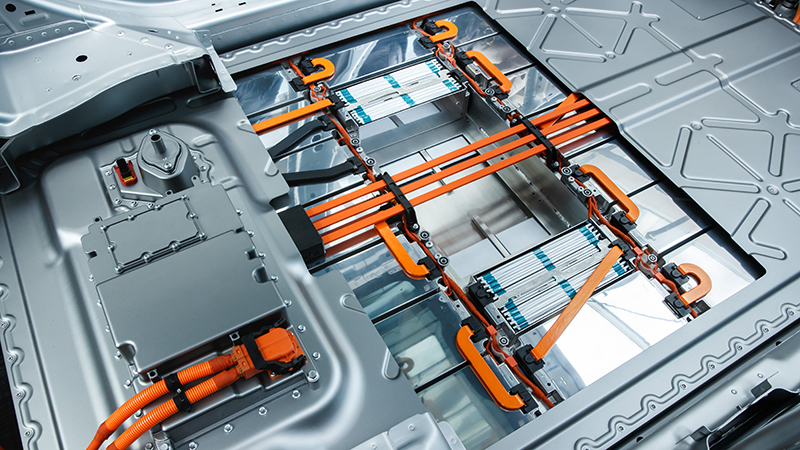
Sure, you’ve heard of lithium-ion batteries. We all have. But what is it? Lithium-ion batteries are commonly used in mobile devices such as cell phones, laptops, and tablets. They’re also used to power electric cars, hybrids, and plug-in hybrids.
The lithium-ion battery is a rechargeable battery also known as an accumulator applied in products requiring a high weight-to-energy ratio, such as sensors and high-performance headphones or smartwatches, or even smartphones. All new electric vehicles are designed with lithium-ion batteries so the vehicles can be recharged using standard electricity sources at home or in public charging stations.
A lithium-ion battery can cost more than $10,000 – so making them lighter and more economical is important
Lithium-ion batteries are expensive. You may be surprised to learn that a typical battery pack for an electric vehicle (EV) can cost over $10,000 or more. In fact, the battery is typically the most expensive part of the EV, accounting for approximately 50% of its total cost.
This means that as technologies improve and EV prices come down, it will probably be because battery costs have dropped enough to make up for it. It’s ok if you don’t know what makes a lithium-ion battery special. Most people don’t. But they are the most common type of rechargeable batteries in EVs. Thousands of scientists and engineers across the globe are trying to improve these batteries so that they can eventually power any vehicle on earth.
Lithium-Ion battery technology is the primary power source for most all-electric vehicles
When it comes to electric vehicles, the heart of the operation is really in the battery technology. Batteries are expensive, so manufacturers are always looking for ways to lighten them and make them more efficient. Lithium-ion batteries are made of lithium and cobalt, two light elements but capable of holding a decent charge. They’ve been used in laptops and cell phones for a while now, but they’re only starting to replace lead-acid batteries in cars because they can be recharged faster.
Bottom Line

EVs have a lot going for them, especially for the batteries that power them. They’re much more energy-efficient than gas-powered cars. This means they don’t have to burn as much fuel and produce as many greenhouse gases and other pollutants that affect our environment and damage our health. They can also hold a charge for longer than traditional gas-powered cars, which means they don’t have to stop as often at charging stations. Besides, they’re less expensive in the long run simply because they use less fuel. The other key advantage is that they’re much quieter than gas-powered cars, so you don’t have to worry about being disturbed by the sounds of your neighbours’ mufflers or engines firing up every morning.

